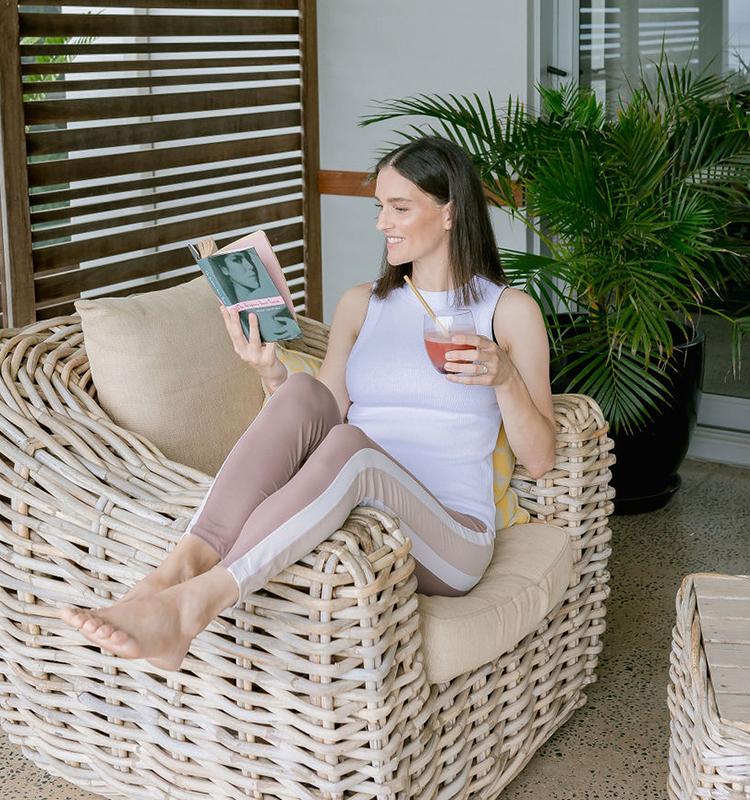
Tuberculosis (TB) has re-emerged to become the world's leading cause of death from a single infectious agent. Inflammatory cytokines play an important role during the course of the disease and may be responsible for tissue damage.
In a clinical study, ginger was found to be effective as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant supplement along with anti-TB therapy as it possesses strong free radical scavenging properties.
Reference:
YuWang Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of ginger in tuberculosis. Applied Nutritional Investigation, vol. 36, 79–84.